It is well known that automating systems often improves the level of convenience for the user. The same is true when it comes to charging electric vehicles. Two technologies exist for automating the charging process: conductive charging and inductive charging. The interface for delivering the electricity is the biggest difference between the two technologies.
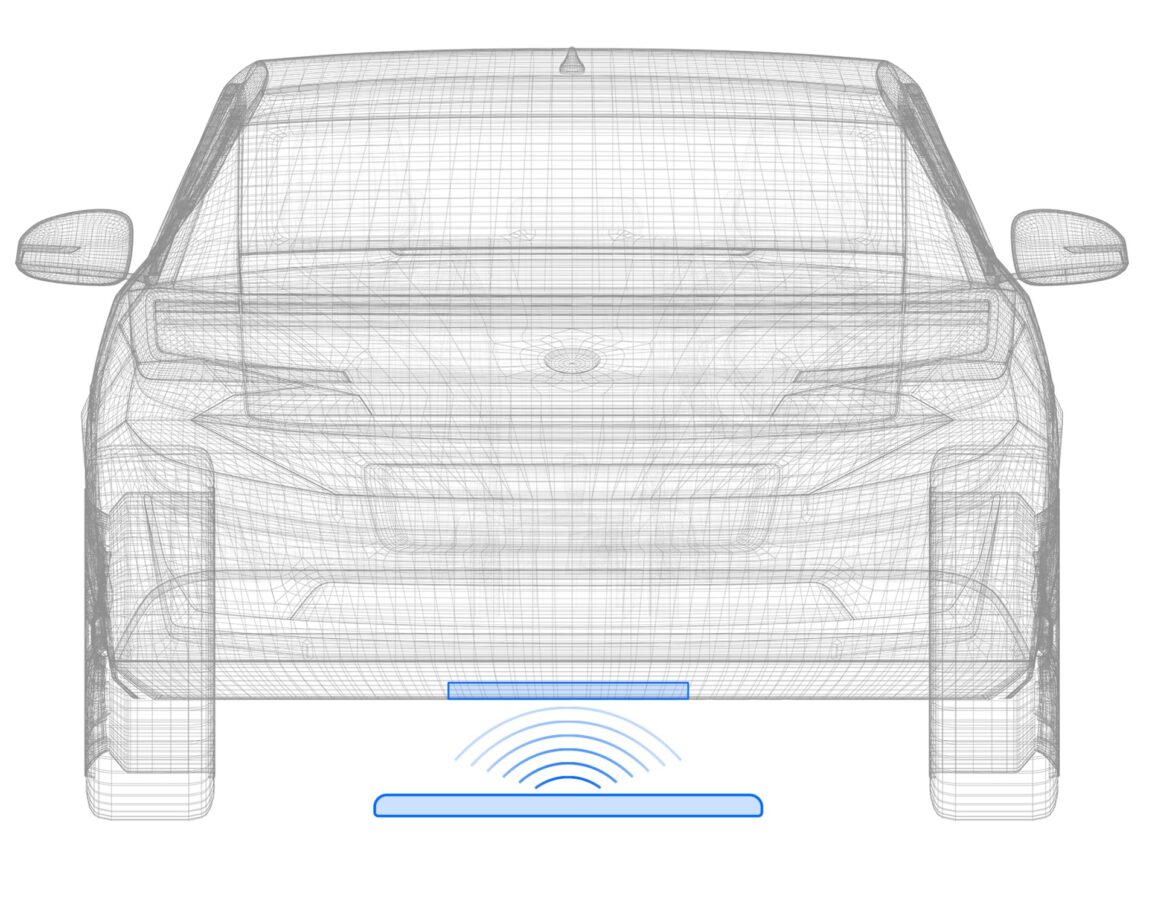
Inductive charging
| With inductive charging, the electricity is delivered entirely without contact by using an electromagnetic field as the energy carrier. The car is charged by creating a magnetic field between a coil in the parking space and another coil in the vehicle undercarriage. Some other examples of inductive charging include induction cooktops, electric toothbrushes and wireless chargers for smartphones. Although surfaces are in contact in all of these applications, there is no actual electrical connection. This means that no electricity flows across the interface, and the transmission of electrical energy takes place entirely via induction. |
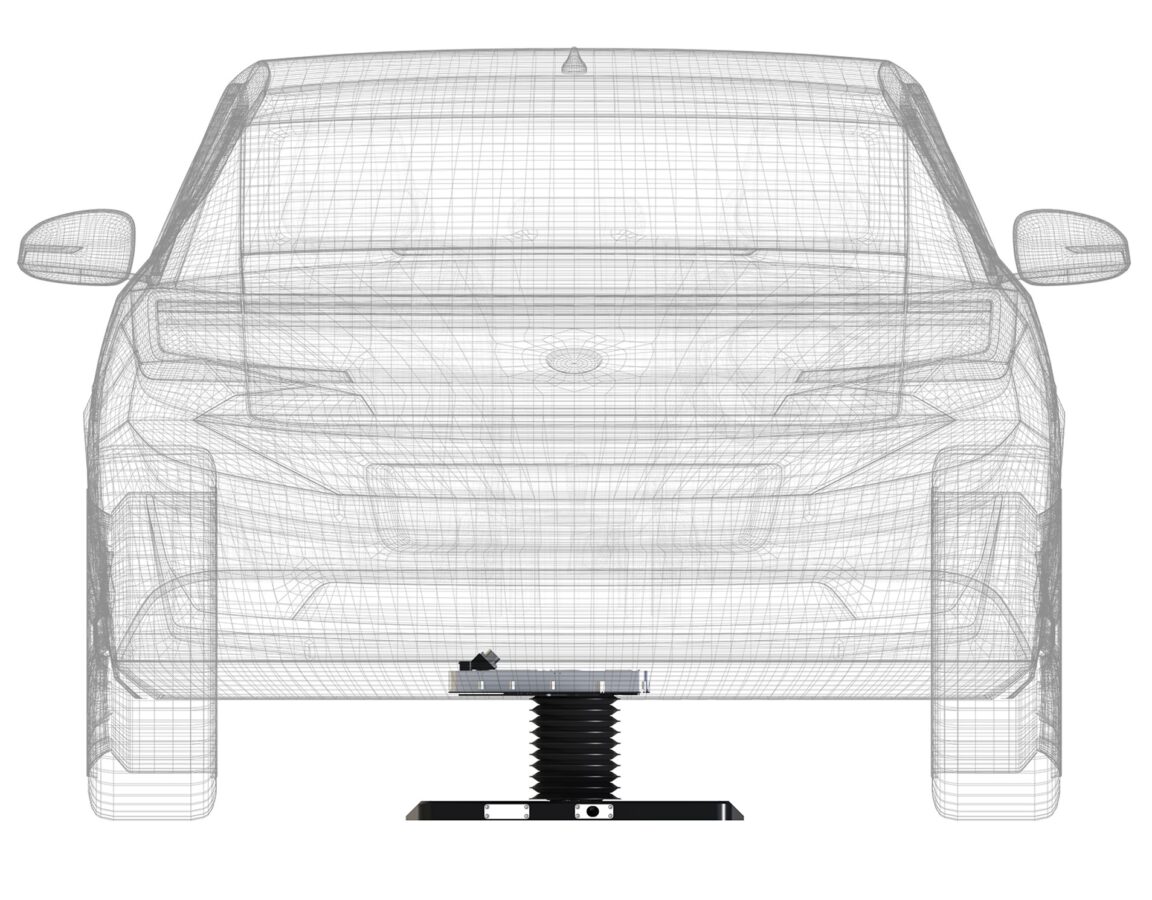
Conductive charging
| In contrast to inductive charging, conductive charging does not allow any air gap between the electrical interfaces. A physical and metallic connection must be established for the charging. Classic charging cables for electric cars, as found in charging stations today, are also based on the conductive transfer of electricity. But the major technological advantage of Matrix Charging® is that the charging process is automated. In other words, there is no need to plug and unplug the cable since the vehicle establishes a connection with a charging plate in the parking space entirely automatically. |
In contrast to conductive charging, inductive charging systems for electric vehicles are associated with high costs for individual components and must get by with limited transmission capacity. Therefore, conductive charging of electric vehicles is the clear solution for maximum efficiency, high energy transfer and low costs. That is why Easelink has developed Matrix Charging® as an automated conductive technology. With Matrix Charging®, the direct physical connection between the conductive contacts results in over 99.8% efficiency for the energy transmission.
Design of the Matrix Charging® technology
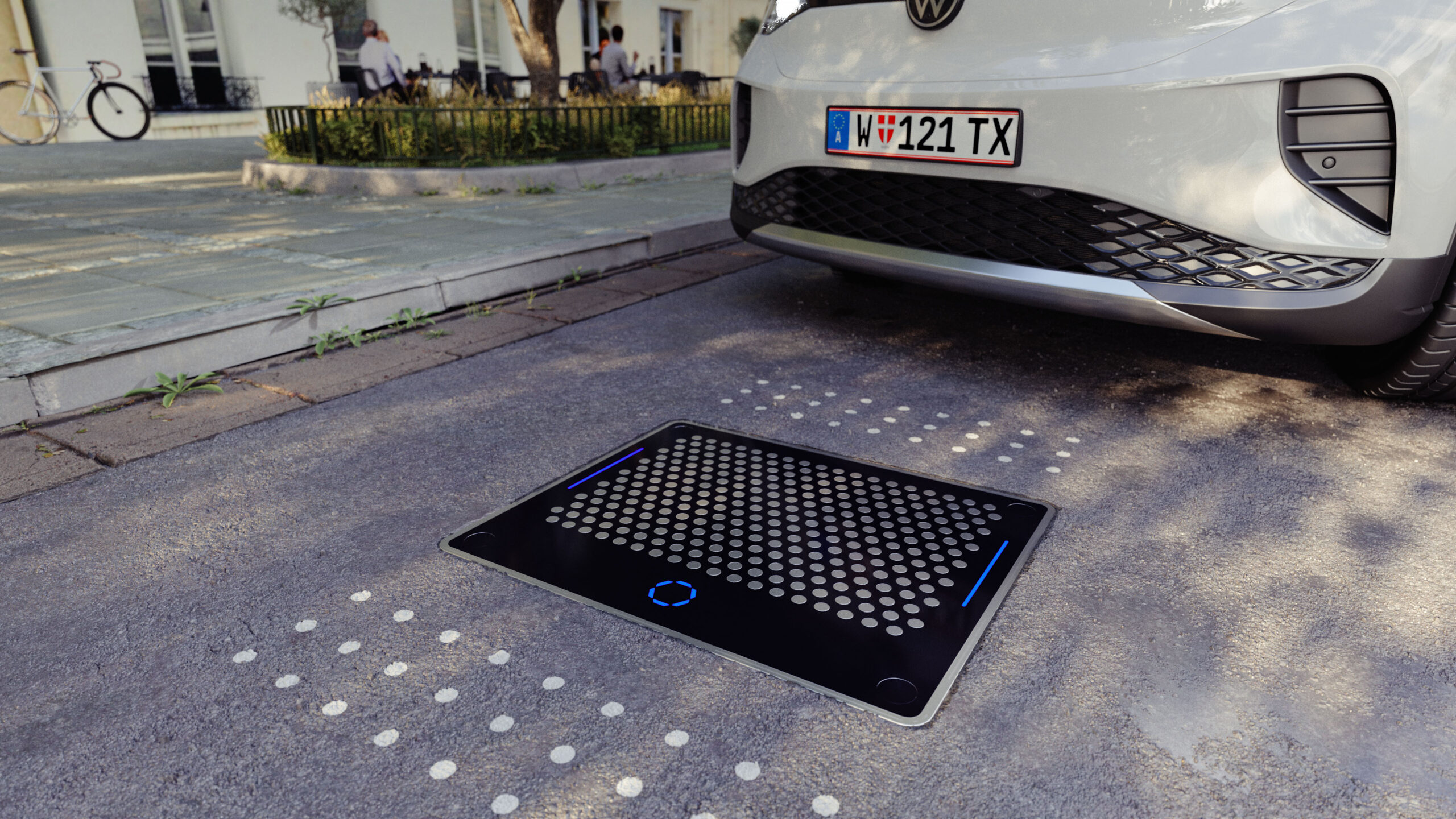
The Matrix Charging® system consists of the vehicle unit on the undercarriage (connector) and an infrastructure unit in the parking space (pad). An array of circular contact points is integrated into the surface of the pad. When the vehicle has parked above the pad, the connector is automatically lowered from the vehicle by a simple vertical movement until it contacts the pad. Once the contact points on the pad that are covered by the connector are activated, the charging begins. This video shows how easy it is to use Matrix Charging®.
Outdoor locations are particularly challenging when it comes to building charging infrastructure because the part of the charging system installed in the parking space must be resistant to weather, dirt, deicing salt and being driven over. If the rollout of charging points in public, semi-public and private environments is to succeed, it is therefore important not to install any complex mechanical systems in the parking space.
Matrix Charging® meets this requirement perfectly. As the infrastructure unit, the pad is exceptionally robust and unaffected by chemical, mechanical, temperature or electromagnetic influences. The pad can even be driven over without sustaining damage. Furthermore, an integrated cleaning function in the connector clears off the pad, removing sand, leaves, gravel, etc. As the connector is lowered down onto the pad, air is automatically blown out through the connector to clear away liquids and debris. Above that, the safety architecture of the system ensures that the pad is safe to touch during the charging process. In other words, there is no danger to any animals (such as cats) who might crawl under the vehicle while it is charging.
Matrix Charging® in cities – no more sacrificing space for charging infrastructure
In addition to increasing the convenience for users and avoiding breakable mechanical components in the parking space, scalability is an essential requirement for a comprehensive rollout of charging points. Therefore, the design of Matrix Charging® supports a rollout for all vehicle segments (from premium to economy vehicles) and in all environments (indoors and outdoors as well as in public and private areas).
The space taken up by typical charging columns in population centers poses difficulties since a lack of space often means that the columns must be installed in the area of the adjoining walkways. However, the minimum walkway widths must still be complied with. In some cases, this encroaches so much on the pedestrian area that little space remains for wheelchairs and baby carriages. In other words, the loss of space reduces accessibility. The visual character of the city is similarly impacted. In historic city districts, consideration must be given to the rules for monument protection and preserving the character of the district.
Implementation of automated charging based on Matrix Charging® offers a host of advantages. The elimination of bulky charging stations and cables allows charging infrastructure to be rolled out even in densely populated areas without taking up any space. The pad can be installed in any parking space without extensive measures. It is robust enough to be driven over and can be installed flush with the surface of the parking space in public areas.
E-mobility offers a way to eliminate carbon emissions from urban traffic. The greatest challenge today is building out the necessary charging infrastructure. Automating the charging connection with Matrix Charging® delivers a high level of user convenience. With the use of Matrix Charging® barriers such as charging columns and suspended charging cables are avoided. Matrix Charging® simplifies the creation of a dense charging network. This in turn facilitates the essential electrification of road vehicles. The project eTaxi Austria is a lighthouse project for promoting the electrification of taxi fleets by implementing automated charging options at taxi stands.

